Gum health: Diagnosis

Diagnosing periodontal disease
Early detection and treatment of periodontitis increases the likelihood of tooth retention.1
Periodontal examination
With the focus on the prevention of dental disease a periodontal examination should form part of every dental visit. Evidence has established that gingival inflammation over time is a key indicator for sites which progress to attachment loss, reinforcing the importance of regular monitoring at dental appointments.2
The WHO originally developed the Community Periodontal Index (CPI) as a way to standardise measurement of the condition to allow for prevalence to be monitored.
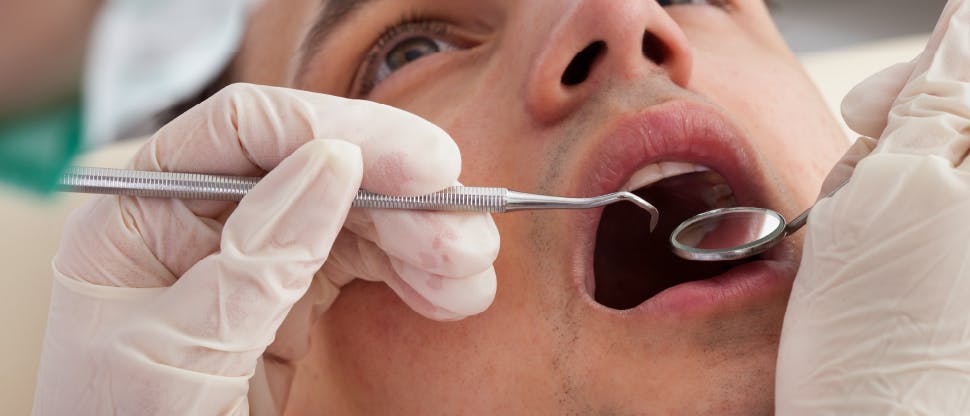
Screening for periodontal disease
In 2017 the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) and European Federation of Periodontology (EFP) convened the World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions to create a consensus knowledge base to be promoted globally. Outputs from this workshop included definitions for gingival health, gingivitis and periodontitis using key measures such as probing depths and bleeding sites.3
Methods of screening vary in their adoption by country but mainly include the following elements:
- Use of 0.5mm ball-tip probe with a marked band between 3.5mm-5.5mm and rings at 8.5mm and 11.5mm from the ball tip
- Light probing force should be used
- The teeth are divided into sextants and each sextant is examined separately
- All sites should be examined and the highest score is recorded for that sextant
- Scores are allocated based on pocket depths and presence of bleeding on probing
- In addition to the 5 numbered scores a * symbol can also be appended to annotate the presence of periodontal abnormalities or furcation involvement
The guidance has been adopted in a variety of ways. Included are 3 examples of practical guidelines created by different periodontal organisations.
The British Society of Periodontology have developed downloadable guidelines for the Basic Periodontal Examination (BPE). Access now.
Discover more about the Comprehensive Periodontal Examination from AAP
Access the FDI Periodontal Diseases chairside guide.
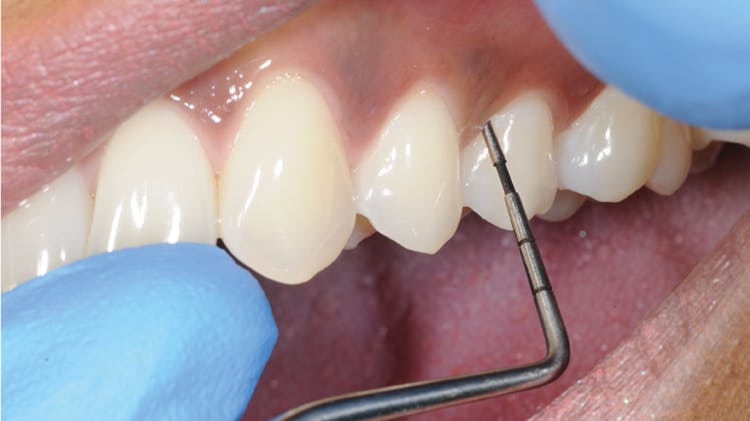
Gingival health
For intact periodontium and reduced and stable periodontium:2No probing attachment loss<10% bleeding sitesProbing depths < 3mm
For successfully treated stable periodontitis patient:Probing attachment loss<10% bleeding sitesProbing depths < 4mm
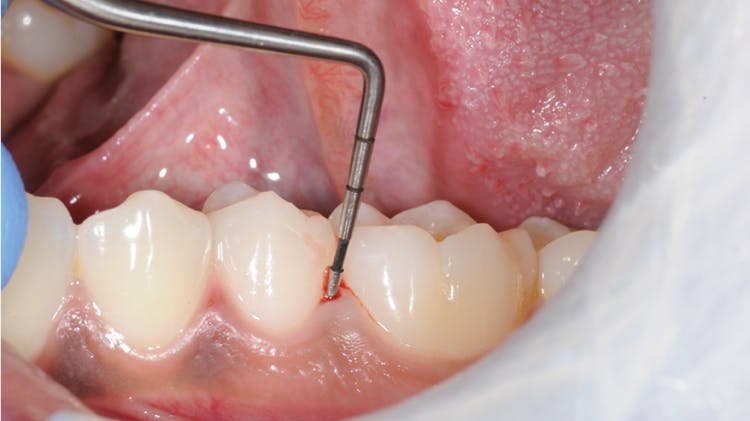
Gingivitis
Intact/reduced periodontium (non-periodontitis patient)2No probing attachment loss>10% bleeding sitesProbing depths < 3mm
In a patient with a history of periodontitis:Probing attachment loss>10% bleeding sitesProbing depths < 3mm
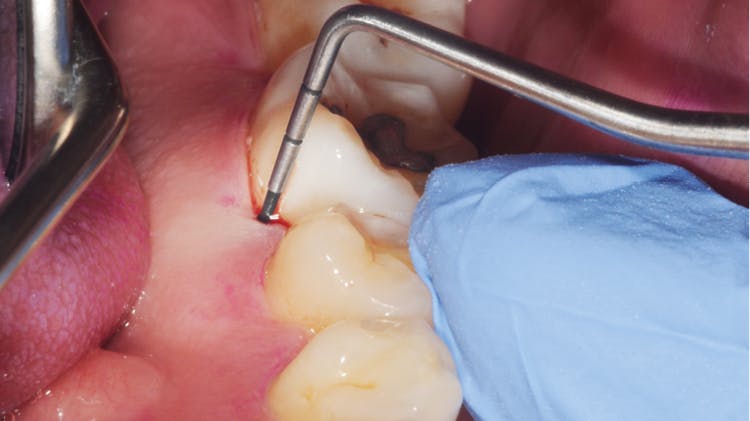
Periodontitis
According to the Consensus Report of Workgroup 2 at the 2017 World Workshop, a patient is a periodontitis case if:4Interdental CAL is detectable at >2 non-adjacent teeth orBuccal or oral CAL >3mm with pocketing >3mm is detectable at >2 teeth and cannot be ascribed to non-periodontitis-related causes.
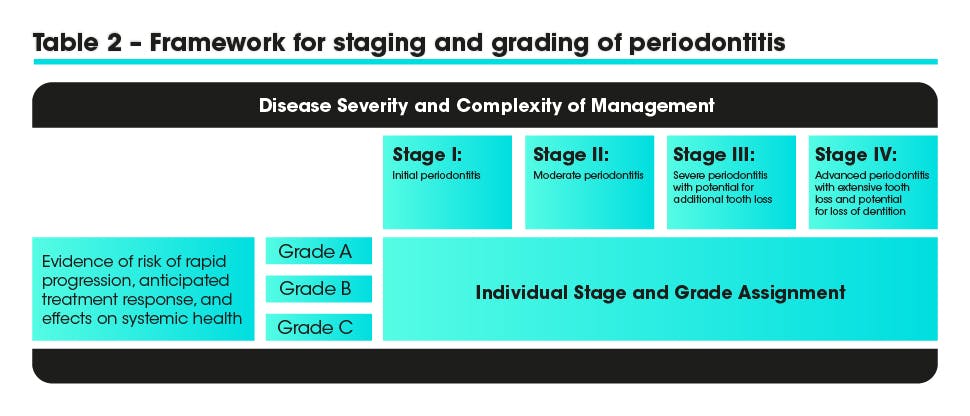
Image Adapted from Consensus Report of Workgroup 2 at the 2017 World Workshop
Staging and Grading Periodontitis
The 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and conditions recommended that periodontitis should be characterized by a new system of multi-dimesional staging and grading.5
Staging:
- Classifies the extent and severity of a patient’s disease
- Measures the amount of destroyed and/or damaged tissue
- Assesses the specific factors that may attribute to the long-term complexity of the case
There are 4 stages which should be determined using clinical attachment loss (CAL) or if this is not available radiographic bone loss (RBL). Tooth loss or complexity factors may increase the level of classification.
Grading:
Aims to indicate:
- The rate of progression
- The responsiveness to standard therapy
- The potential impact on systemic health
There are 3 grading levels A-C and primary criteria include radiographic bone loss or CAL or if this is not available %bone loss/age and case phenotype can be used.
Access a summary of staging & grading periodontitis on the AAP website
You can access the EFP clinical decision tree for staging and grading here
Help your patients on their journey to optimal gum health
Causes and mechanisms
Find out about the causes and mechanisms behind periodontal disease.

Patient behaviour change
parodontax has been working with behaviour change professionals and patients to find out how – collectively – we can inspire the habits that improve gum health and help prevent gum disease.
