Advil Tablets
Advil oral pain products deliver superior relief vs other analgesics like acetaminophen in Tylenol
Experts and patients have trusted Advil for effective pain relief for 40+ years.
Clinical studies show that the medicine in Advil oral products is a superior pain reliever compared to acetaminophen. And when used as directed, Advil also has a proven safety profile.
Advil oral products are clinically proven to provide relief for a variety of pain conditions. They are indicated for the temporary relief of minor aches and pains due to:
- Headache
- Toothache
- Backache
- Menstrual cramps
- The common cold
- Muscular aches
- Minor pain of arthritis
- The temporary reduction of fever

Advil is tough on acute pain and easy on your patients
Advil oral products are more effective than Tylenol® for treating tough acute pain. In fact, no other over-the-counter (OTC) pain reliever has been shown to be more effective than ibuprofen.*
*Among leading OTC pain relievers/fever reducers. Remind patients to use OTC analgesics as directed.
Proven superiority, fast onset
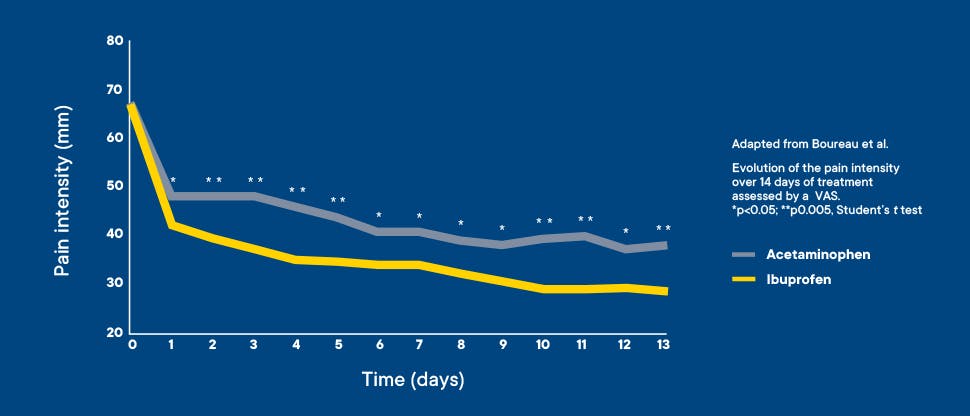
Clinical studies of dental pain, pain from the common cold, tension-type headaches, and muscle soreness have demonstrated that ibuprofen (Advil) is more effective than acetaminophen (Tylenol).
An additional study in osteoarthritis (OA) showed that ibuprofen provided a greater decrease in pain intensity than acetaminophen did after the initial dose. The same study also concluded that over the course of 14 days, ibuprofen provided greater sustained pain relief and significantly greater efficacy versus acetaminophen.
Advil for a headache
Headaches affect about 95% of people at some point, with nearly half of adults experiencing one each year. They account for 1 in 10 visits to a healthcare provider, 1 in 3 neurology referrals, and 1 in 5 acute medical admissions. The World Health Organization ranks headache among the top 10 causes of disability, with an impact comparable to arthritis and diabetes, and greater than asthma.
Primary headache disorders constitute most headache disorders, with tension-style headache.
Healthcare providers can feel confident in recommending Advil tablets for headache management.
NSAIDs for headaches
A randomized, double-blind study from the Journal of Head and Face Pain of 660 adult outpatients with moderate to severe headaches evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of single-dose ibuprofen at 200 mg or 400 mg compared with placebo.
At 2 hours post-dose, significantly more patients receiving ibuprofen achieved pain reduction to mild or none versus placebo. Both ibuprofen doses demonstrated greater mean pain intensity difference from baseline at 2 hours and at 1 hour post-treatment.
When evaluating whether to prescribe NSAIDs for headaches, single doses of ibuprofen 200 mg and 400 mg are effective, well-tolerated nonprescription treatments for headache pain, with additional benefits for associated symptoms.

Advil has a favorable safety profile
As with any medication, there are risks associated with the use of ibuprofen. However, research has shown that ibuprofen at OTC doses has a proven safety profile. A recent review confirmed that at OTC doses, ibuprofen has a low incidence of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events and minimal risk of causing renal and associated cardiovascular events, among others.
Also, when used as directed, ibuprofen 400 mg has a favorable GI safety profile. There is a dose relationship with risk for adverse events with ibuprofen and other NSAIDs, which are generally well tolerated at lower OTC doses.
For patients with any of the risk factors below, doctors should discuss the individual benefits/risks of using NSAIDs.
| Active Ingredient (in each Advil Tablet) | Purpose | Directions |
| Ibuprofen 200 mg (NSAID)**nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
Pain reliever/ Fever reducer
|
Advil dose for adults and children 12 years and over:
Children under 12 years old should not take Advil tablets without first consulting a doctor. Advil dosage per day: Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours, unless directed by a doctor. Always read the label. |
Gastrointestinal: Advil was observed to have a low risk of serious GI events in clinical studies
Ibuprofen has a favorable gastrointestinal (GI) safety profile at dosages of 800 mg to 1200 mg per day (in OTC dose).
Clinical studies have shown that when OTC ibuprofen is taken as directed by the label for no longer than 10 days, there is a low increased risk of stomach complaints or bleeding.
- A recent literature review found that in OTC doses of ibuprofen, there was a consistently low risk of serious GI events and that nonserious GI events are probably reversible upon cessation of the drug
- An epidemiologic study by Lewis et al and a systematic review by Henry and McGettigan found no significant increased risk of serious upper GI toxicity at dosages <1200 mg daily
- In a study by Moore et al, more subjects reported significant digestive adverse events for 1 to 7 days with aspirin (7.1%) or acetaminophen (5.3%) than with ibuprofen (4.0%)
- Studies have demonstrated that higher doses of ibuprofen (and other NSAIDs) are associated with a greater risk of GI side effects (odds ratio 4:6) vs lower (OTC) doses (odds ratio 1:1)
Advil tablets safety: cardiovascular
Cardiovascular: Advil presents minimal cardiovascular risk as observed in clinical studies
Several medical publications have evaluated the cardiovascular safety profile of ibuprofen, the active ingredient in Advil, at OTC doses
A comprehensive review of existing cardiovascular safety data shows that when ibuprofen is used at doses according to label directions, cardiovascular risk is minimal.
Data from a series of publications suggest that OTC ibuprofen is not strongly associated with an increased risk of:
- Cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction [MI], stroke)
- Cardiorenal events (high blood pressure, congestive heart failure)
However, multiple studies have found that taking ibuprofen or other NSAIDs at Rx doses over prolonged periods can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular events.
Advil tablets safety: renal
Renal: The medicine in Advil has a low risk factor for developing renal conditions as observed in clinical studies
Clinical evidence suggests over-the-counter (OTC) ibuprofen has a low risk factor for developing acute or chronic renal conditions.
Advil tablets safety: hepatic
Hepatic: Advil demonstrates a low risk of hepatic injury
The use of over-the-counter (OTC) ibuprofen demonstrates a low risk of developing liver injury, especially compared with the severe liver damage observed with acetaminophen overdose and the occasional liver reactions from aspirin.
Recommend Advil for clinically proven, effective pain relief with a favorable safety profile
Learn more about Advil and pain relief

Overview of pain conditions
Learn about common pain conditions such as OA pain, headache, sprains and strains, and more, and discover how Advil can give your patients relief.
Patient care resources
Access educational resources for your patients, to help them have a better understanding of their pain condition.
