Gum Disease: Causes and Mechanisms

The role of plaque in gum diseases
Following extensive studies it is universally agreed that periodontal diseases are initiated by plaque bacteria.1
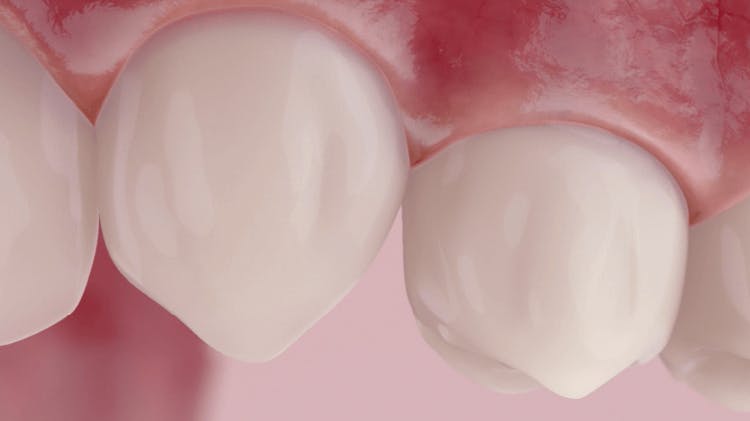
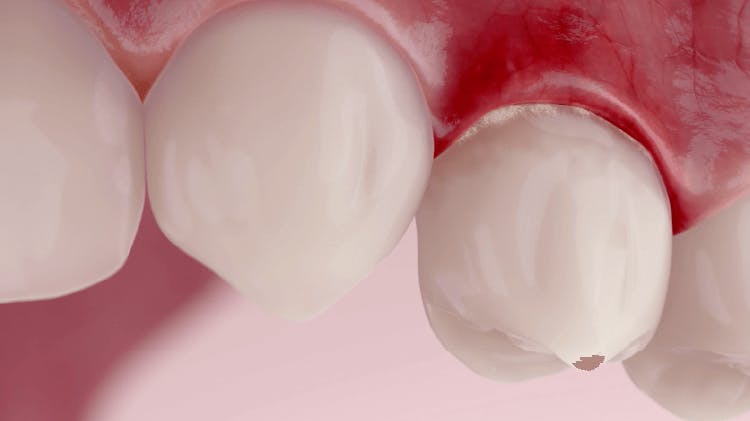
Early symptoms such as swollen, red and bleeding gums (gingivitis) result from the reversible inflammatory response triggered in the gingival tissues by the toxins in the plaque biofilm.1,2 However, the level of plaque accumulation necessary to induce gingival inflammation and impact its progression varies by patient.3
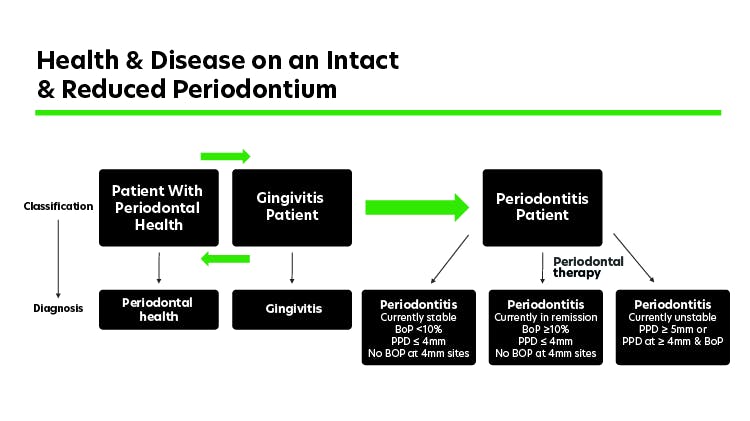
In 2017 the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) and European Federation of Periodontology (EFP) convened the World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions to create a consensus knowledge base to be promoted globally. In the consensus report of workgroup 1 it was concluded that gingivitis “is a non-specific inflammatory condition and is therefore a consequence of sustained plaque biofilm accumulation at an apical to the gingival margin”.3 The report also highlighted that “plaque is a major risk factor, and necessary pre-requisite for periodontitis and therefore management of gingivitis needs to be a primary prevention strategy for periodontitis”.3
The World Workshop outputs highlighted that patients with a history of periodontitis are “at a lifelong high risk of recurrent periodontitis” and will require site-specific monitoring as part of a maintenance programme.
So whilst poor oral hygiene and the resulting presence of plaque is the main cause of periodontal diseases it is not the sole causal factor for the progression of periodontitis.
Causes of periodontal disease patient video
This video outlines the main causes of periodontal disease and can be shared with patients in line with your advice.

What determines the rate of development, severity and extent of gum disease?
In addition to plaque accumulation, there are a number of local (predisposing) and systemic (modifying) factors which may mean patients are more at risk of disease progression.3 These were outlined as part of the 2017 World Workshop to provide a consolidated list and can be used to help inform risk assessment for patients.
As part of the global periodontal health project, the FDI has created a disease prevention and management chairside tool. Find out more here.

Local risk factors from AAP & EFP Global Classification
These are factors which either encourage plaque accumulation or in some way inhibit plaque removal and include:3
- Factors which retain plaque accumulation and make it difficult to remove plaque through brushing and interdental cleaning e.g. malpositioned teeth or restorations3
- A lack of salivary flow. Conditions such as xerostomia may mean a reduced cleansing of tooth surfaces and leave patients at risk. Causes of xerostomia include medication use and conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome3

Systemic risk factors from AAP & EFP Global Classification
Systemic risk factors are also known as modifying risk factors as they relate to the individual’s characteristics of the patient which may influence their immune-inflammatory response to plaque biofilm.3
- Smoking has profound effects on the gingival tissues which can mask the clinical signs of gingivitis such as bleeding on probing despite inflammatory cell responses3
- Metabolic factors including hyperglycemia in people with or without diabetes3
- Nutritional factors including severe vitamin C deficiency
- Pharmacological agents can also increase susceptibility to gingivitis. This may be due to reduced salivary flow, impact endocrine function or induce gingival enlargement
- Hormonal changes related to sex steroids e.g. puberty or pregnancy can modify the gingival inflammatory response
- Hematological conditions e.g. leukemia can lead to excess gingival inflammation
Periodontitis shares common risk factors with other non-communicable diseases
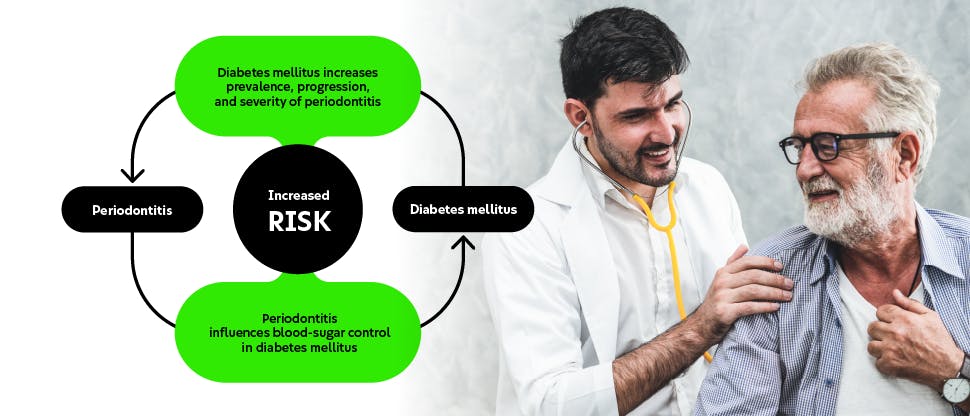
Periodontitis is a non-communicable disease (NCD) and shares common risk factors with other NCD’s including smoking, being overweight, glycaemia/hyperglycaemia and stress.
Evidence is building to support the fact that management of lifestyle factors associated with many NCDs can also reduce periodontal disease. A systematic review by Ramseier et al4 highlights the evidence that smoking cessation, diabetes control, increase in physical activity, dietary adjustments and weight loss improve periodontal health and the patients’ quality of life.
There are strong associations (a two-way relationship) between diabetes and periodontitis. People with periodontitis have a higher risk of diabetes and patients with periodontitis are three times more likely to develop periodontal disease.5 In addition, controlling diabetes is more complicated when a patient also has periodontitis.5
Recent studies indicate the rate of developing periodontitis increases 1.8 times more in obese individuals, and those with a BMI > 30 were three times more likely to develop periodontitis.6,7 Worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975.8
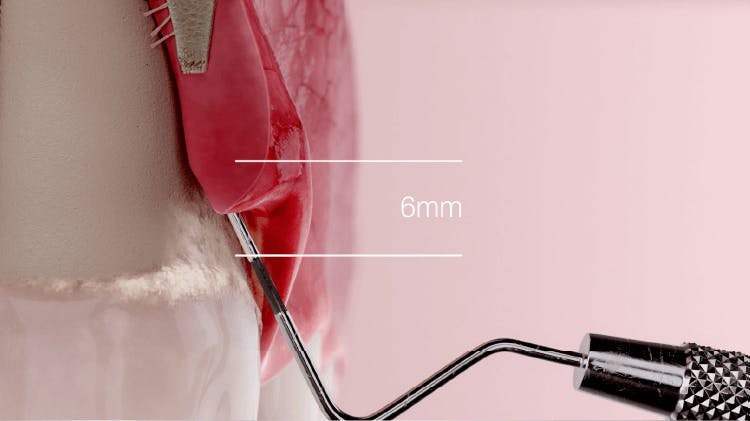
The progression of periodontal disease
Help your patients on their journey to optimal gum health
Impact on patient quality of life
Find out about the impact periodontal disease has on patients’ daily lives.