Joint and osteoarthritic pain: Causes

Understand joint pain, including osteoarthritis
Joint pain may be acute or chronic and be associated with a multitude of possible aetiologies.1–3
Here we review some of the potential causes of pain emanating from joint tissues.
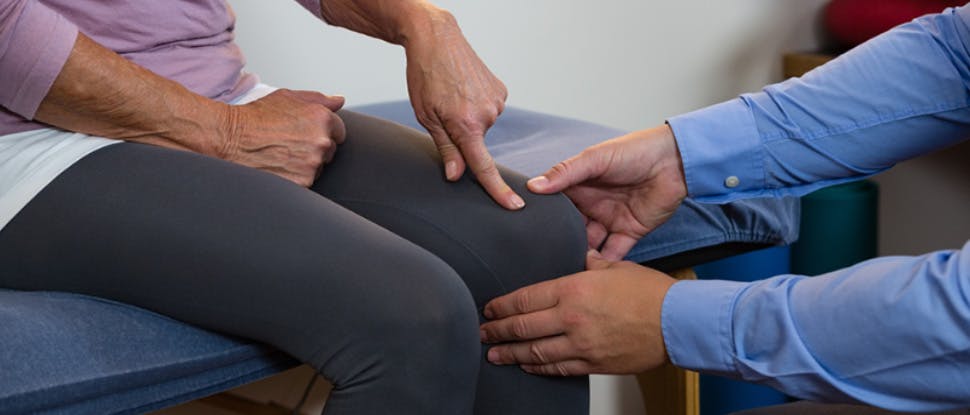
Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of worsening joint pain4,5
Osteoarthritis is characterised by structural changes within the whole joint – as caused by a multitude of pathogenic factors6–8
- Mechanical: changes in cartilage composition increase its susceptablility to force-induced erosions
- Metabolic: activation of cell-signalling pathways in response to damage leads to further joint degradation
- Inflammatory: metabolic activity initiates a proinflammatory response
This complex process ultimately leads to structural destruction and failure of the synovial joint.8

Other conditions may also cause joint pain
Aside from osteoarthritis, a range of conditions can cause joint pain. Acute joint pain, for example, may arise from soft-tissue injuries such as sprains and strains, or overuse injuries or infection.2,3,9 Chronic joint pain however, may be associated with conditions such as tendonitis, bursitis or various forms of arthritis.2–4,10
Soft-tissue injuries are a common cause of acute joint pain. These can include sprains occurring during sports, and overuse injuries.9
Risk factors for osteoarthritis

Certain risk factors for osteoarthritis are known
Although the exact cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, certain factors increase its risk:8,11–13
- Being over 45
- Being female
- Increased body weight (particularly affects the knees)
- Family history of osteoarthritis or bone abnormalities
- Socioeconomic status
- Injury or overuse of joints (e.g. in athletes)
- Previous joint trauma (particularly affects the knees)
- Muscle weakness
Understanding joint pain and osteoarthritis
Signs and symptoms
Explore an overview of how to recognise joint pain and osteoarthritis and know when to refer patients.
Learn more
Voltarol Joint & Back Pain Relief 2.32% Gel Diclofenac Diethylammonium
All day joint pain relief when applied morning and night.

Voltarol Osteoarthritis Joint Pain Relief 1.16% Gel Diclofenac Diethylammonium
Proven to be as effective as ibuprofen tablets for localised joint pain.14
