Allergic Rhinitis Management

A tailored approach to allergic rhinitis (AR) treatment
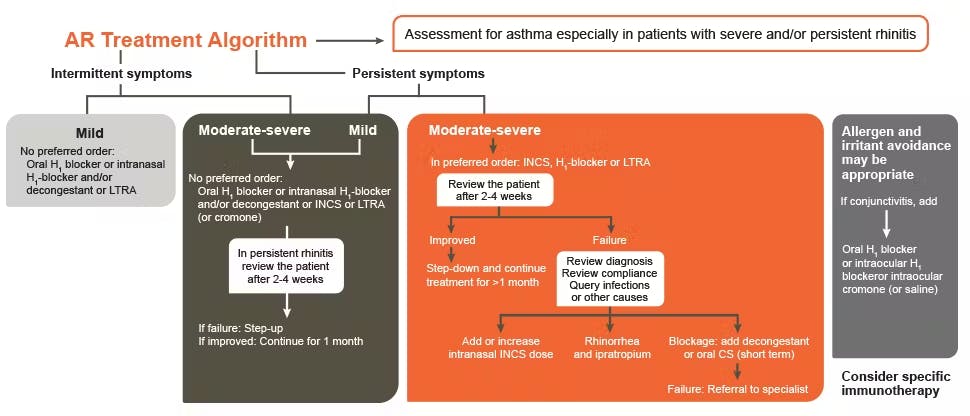
ARIA AR treatment algorithm1
The management of AR should be tailored according to the severity of the disease, co-morbidities, treatment availability and affordability, and the patient’s preference.1
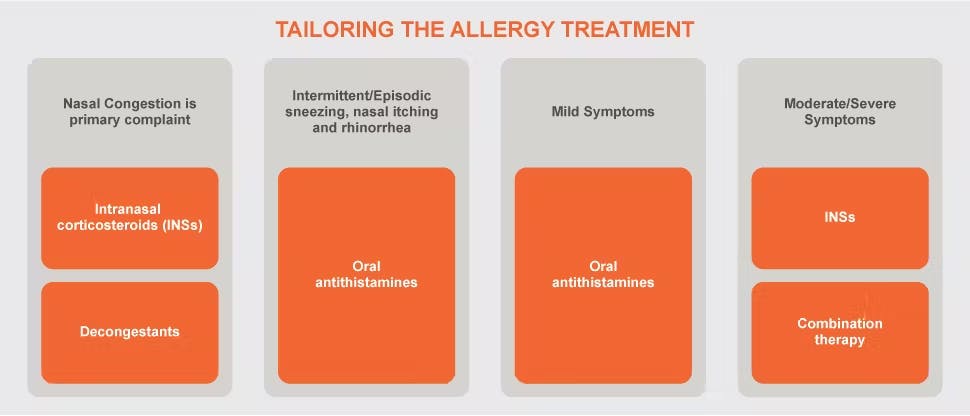
Simplified AR treatment algorithm
Recommendations from the AAAAI (American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology)
- The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) issued practice parameters for treating rhinitis in 2008. These guidelines suggest that pharmacotherapy treatment should be individualized and depends on a variety of factors, including3:[Wallace, pS8B]
- Type of rhinitis—seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR), perennial allergic rhinitis (PAR), or Nonallergic rhinitis (NAR)
- Symptoms, their duration, and their severity
- Physical exam findings
- Comorbidities
- Age
- Patient preferences
Overall, the AAAAI recognizes INSs are recognized as the most effective class for controlling symptoms of long-term treatment for AR3
Pharmacological options
| Intranasal steroids | Fluticasone propionate, triamcinolone acetonide, budesonide | |
| Intranasal combination sprays | Azelastine/fluticasone propionate | |
| Antihistamines | Centirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, clemastine, diphenhydramine | |
| Decongestants | Pseudoephedrine, oxymetazoline hydrochloride, zinc acetate/zinc gluconate, oxymetazoline | |
| Anticholinergics | Ipratropium bromide | |
| Antileukotrienes | Montelukast | |
| Chromones/cromoglycates | Cromolyn sodium | |
The most commonly used medications in the treatment of AR are4:
Although each treatment option will help to reduce a person’s AR symptoms, clinicians should tailor the treatment option. Each of the following scenarios would have different considerations2:
- Person with nasal congestion as the primary complaint
- Person with intermittent or episodic nasal AR symptoms
- Person with mild AR symptoms
- Person with moderate to severe AR symptoms
ICSs are considered the most effective treatment for moderate intermittent and all stages of persistent rhinitis and for all nasal symptoms, ocular symptoms, polyposis, and sinusitis.5
INSs demonstrate low systemic absorption, although some systemic side effects may occur, including immunosuppression and slower growth in pediatric use.12-14
The role of INSs in the treatment of AR: According to the algorithm pharmacological options
According to the 2008 Rhinitis Updated Practice Parameter from the AAAAI, INSs are the most effective first-line medication class for controlling symptoms of AR.3
- In the treatment of SAR, INSs have been shown to be more effective than the combined use of an antihistamine and a leukotriene (LT) antagonist. 3
- INSs may provide significant symptom relief for patients with SAR, whether they’re used on a regular basis or on an as-needed basis.3
Read more about allergic rhinitis
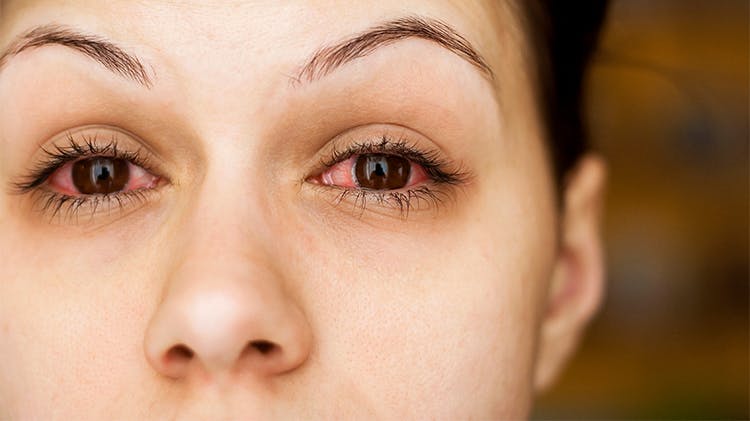




Impact on Patient Quality of Life
Find out about the impact allergic rhinitis has on patients’ daily lives


Otri Allergy products
Find out how our products can help your patients suffering from allergic rhinitis