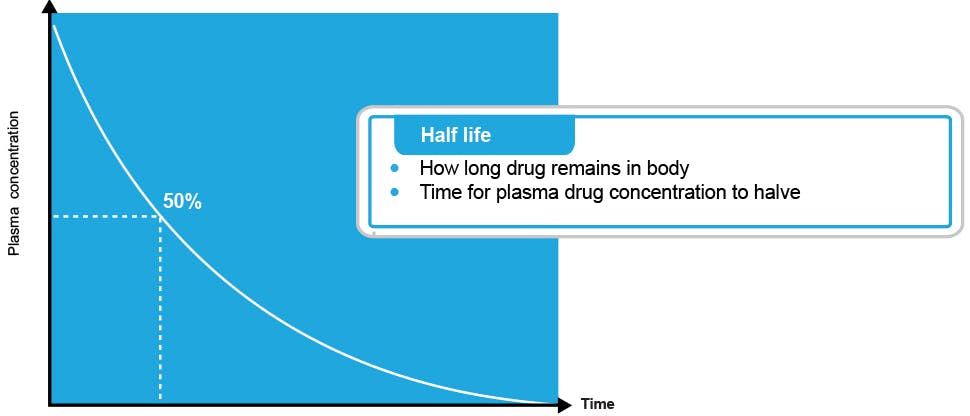
The science of paracetamol
Paracetamol exerts its analgesic and antipyretic effect primarily by inhibition of prostaglandins. Unlike non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), it does not have anti-inflammatory properties and therefore has a different tolerability profile.1

Paracetamol basics
Globally, paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen) is one of the most used analgesic and antipyretic over-the-counter drugs. Both its names are derived from its chemical name, which is N-acetyl-para-aminophenol.1 From the time of its first introduction in 1955 for use in children with fever and pain, paracetamol has been formulated as a single compound or as an active ingredient in combination with other drugs, such as caffeine.1,2
When paracetamol is taken as indicated, minimal serious side effects have been observed.16
Discover the Panadol range with paracetamol
Panadol with Optizorb technology
Absorbed faster than standard Panadol tablets to provide pain relief.18,19¶
Panadol Rapid for fast relief†
Absorbed 2X faster than standard Panadol tablets, Panadol Rapid offers fast pain relief of acute pain.5,20†

Effective children’s fever and pain relief,21-23 gentle on the stomach24,25*
Containing paracetamol, which can be used in children as young as 1 month of age,26-28 paracetamol in Children’s Panadol can start to reduce fever in 15 minutes.29,30‡